![]() Definition :
Definition :
Normal distributions are a family of distributions that have the same general shape. They are symmetric with scores more concentrated in the middle than in the tails. Normal distributions are sometimes described as bell shaped. Examples of normal distributions are shown to the right in Fig 1. Notice that they differ in how spread out they are. The area under each curve is the same. The height of a normal distribution can be specified mathematically in terms of two parameters: the mean and the standard deviation (s).
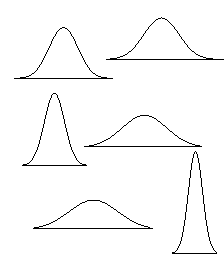
Fig. 1 - Normal Distribution
![]() Formula :
Formula :
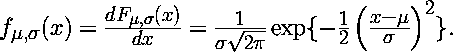
The standard normal distribution
is symmetric about the origin and hence µ = 0. Also σ = 1. Hence the formula
becomes
![f(x) = EXP[-x**2/2]/SQRT(2*PI)](images/norpdf.gif)
![]() Application :
Application :
One reason the normal distribution is important is that many psychological and educational variables are distributed approximately normally. Measures of reading ability, introversion, job satisfaction, and memory are among the many psychological variables approximately normally distributed. Although the distributions are only approximately normal, they are usually quite close. A second reason the normal distribution is so important is that it is easy for mathematical statisticians to work with. This means that many kinds of statistical tests can be derived for normal distributions. Almost all statistical tests discussed in this text assume normal distributions. Fortunately, these tests work very well even if the distribution is only approximately normally distributed. Some tests work well even with very wide deviations from normality. Finally, if the mean and standard deviation of a normal distribution are known, it is easy to convert back and forth from raw scores to percentiles.
![]() Applet :
Applet :
For an illustration of normal distributions go to
http://www.stat.stanford.edu/~naras/jsm/NormalDensity/NormalDensity.html
http://psych.colorado.edu/~mcclella/java/zcalc.html
![]() Excel Function :
Excel Function :
These functions can be accessed by clicking on Insert and then choosing Function from the drop down menu.
The Excel function for finding a normal distribution for a given data set is :
Normdist(x,mean,standard_dev, cumulative)
This returns the normal cumulative distribution for the specified mean and standard deviation.
![]() Further comments :
Further comments :
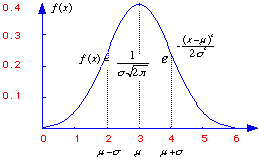
The standard normal distribution is a
normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
Normal distributions can be transformed to standard normal distributions by the
formula:
![]()
where X is a score from the original normal distribution, μ is the mean of the original normal distribution, and σ is the standard deviation of original normal distribution. The standard normal distribution is sometimes called the z distribution. A z score always reflects the number of standard deviations above or below the mean a particular score is. For instance, if a person scored a 70 on a test with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 10, then they scored 2 standard deviations above the mean. Converting the test scores to z scores, an X of 70 would be:
![]()
So, a z score of 2 means the original score was 2 standard deviations above the mean. Note that the z distribution will only be a normal distribution if the original distribution (X) is normal.
Applying the formula
![]() will always
produce a transformed variable with a mean of zero and a standard deviation of
one. However, the shape of the distribution will not be affected by the
transformation. If X is not normal then the transformed distribution will not be
normal either. One important use of the standard normal distribution is for
converting between scores from a normal distribution and
percentile ranks.
will always
produce a transformed variable with a mean of zero and a standard deviation of
one. However, the shape of the distribution will not be affected by the
transformation. If X is not normal then the transformed distribution will not be
normal either. One important use of the standard normal distribution is for
converting between scores from a normal distribution and
percentile ranks.
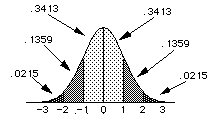
Areas under portions of the standard normal distribution are shown to the right.
About .68 (.34 + .34) of the distribution is between -1 and 1 while about .96 of
the distribution is between -2 and 2.
The above material has been taken from
http://davidmlane.com/hyperstat/normal_distribution.html